Bed Bugs vs. Fleas
Bed bugs and fleas are common household pests with distinct differences. Bed bugs are reddish-brown, wingless insects that feed on human blood, often causing itchy, red welts. They are notorious for hiding in small crevices and being active at night. Fleas, smaller and darker, primarily feed on pets but can also bite humans. They are known for their powerful jumping ability. While both pests don’t directly transmit diseases to humans, their bites can lead to allergic reactions and secondary health issues. Homeowners should focus on prevention, such as regular cleaning and inspecting second-hand furniture for bed bugs, and regular pet grooming for flea control. If infestations occur, professional pest control is often necessary.

In the quiet corners and hidden spaces of our homes, a silent war is often waged. Unseen to the naked eye, tiny invaders make their way into our living spaces, turning our places of comfort and safety into unexpected battlegrounds. Among these stealthy intruders, bed bugs and fleas are particularly notorious, known for their resilience and ability to disrupt our daily lives. These minuscule pests, though often lumped together in the public mind, present unique challenges and require distinct strategies to manage effectively.
Bed bugs, with their flat, oval bodies, have haunted human habitats for centuries, emerging at night to feed on our blood. Their bites, often mistaken for other insect bites, can lead to a range of reactions from mild irritation to severe allergic responses. The psychological impact of knowing these creatures share your bed can be just as distressing as the physical discomfort they cause.
Fleas, though commonly associated with pets, are equally adept at making human hosts uncomfortable. These tiny, dark parasites, armed with powerful legs, can leap into our lives, bringing with them a host of problems. Their bites are itchy and irritating, and their presence can be a sign of broader issues, particularly if pets are part of the household.
Bed Bugs vs. Fleas At A Glance
Bed Bugs
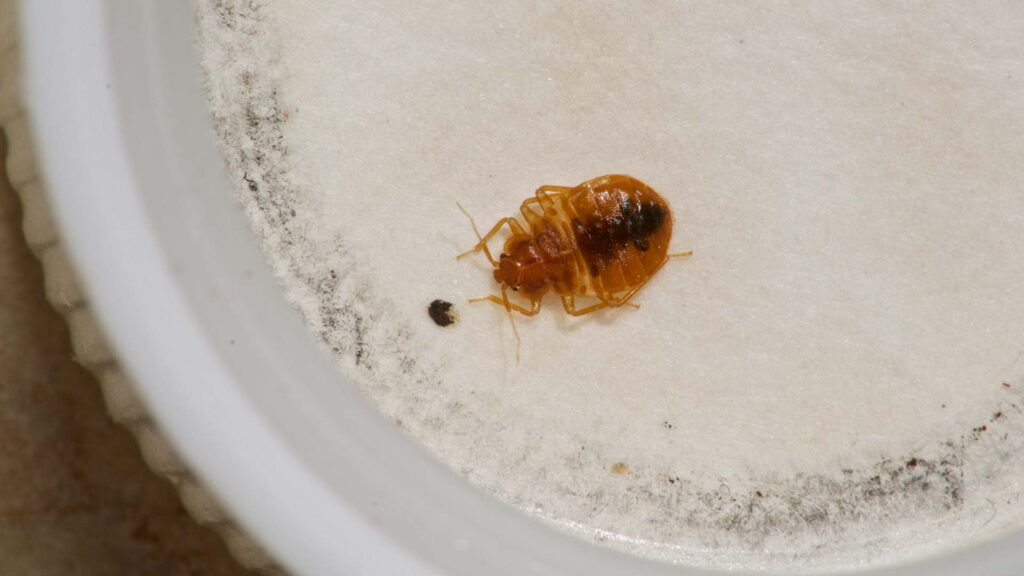
- Small, reddish-brown, oval-shaped insects.
- About the size of an apple seed (5-7 mm).
- Bite marks are small, red, and often in a line or cluster.
- Primarily found in mattresses, bed frames, and furniture.
- Mostly nocturnal, feeding on human blood at night.
Fleas
- Tiny, dark brown, and wingless.
- Smaller than bed bugs, around 1.5-3.3 mm.
- Bite marks are tiny, red, and randomly scattered.
- Commonly found on pets, in pet bedding, and carpets.
- Known for their jumping ability; feed on blood from pets and humans.
The distinction between these two pests is crucial for homeowners. Each requires a different approach in terms of detection, prevention, and eradication. Misidentification can lead to ineffective treatment methods, allowing the problem to proliferate and potentially causing increased emotional and financial strain.
Understanding the habits, preferences, and weaknesses of these pests is the first step in reclaiming your home from these unwelcome guests. This guide aims to arm homeowners with the knowledge needed to identify, prevent, and tackle infestations of bed bugs and fleas, ensuring the safety and comfort of their living spaces.
Bed Bugs vs. Fleas: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to household pests, bed bugs and fleas are often mentioned in the same breath. However, these two pests have distinct characteristics and behaviors that are important for homeowners to understand in order to effectively tackle an infestation.
Bed bugs are small, oval, brownish insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. Adult bed bugs have flat bodies about the size of an apple seed, but after feeding, their bodies swell and are a reddish color. They do not fly, but they can move quickly over floors, walls, and ceilings.
Fleas, in contrast, are smaller and darker than bed bugs. They are about the size of a pinhead and have a shiny, reddish-brown color. What sets fleas apart is their long hind legs, designed for jumping. Fleas are capable of jumping as high as 13 inches, making them some of the best jumpers of all known animals (relative to body size).
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal and are most active at night when they feed on the blood of sleeping humans. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide, which is why they are often found in bedding or mattresses. Bed bugs are known for their stealthy behavior; they can feed unnoticed and retreat to their hiding spots, which are often in cracks, crevices, and within bedding.
Fleas, on the other hand, are more commonly associated with pets. They feed on the blood of animals and humans and are often brought into the home on pets. Unlike bed bugs, fleas remain on their host for a while, making them easier to spot on pets. They are also known for their rapid reproduction; a single flea can lay hundreds of eggs, leading to a quick infestation.
The bite patterns of bed bugs and fleas can help in identifying the pest. Bed bug bites often appear in a line or cluster, usually on the upper body, neck, arms, and shoulders. These bites can be itchy and may cause allergic reactions in some people.
Flea bites, conversely, are usually located on the lower body, particularly around the ankles and legs. They are small, red, and can be extremely itchy. In pets, flea bites can lead to excessive scratching, hair loss, and irritation. Fleas can also transmit diseases to pets, such as tapeworms and, in rare cases, can carry diseases that affect humans.
Bed bugs are often spread through travel. They hitchhike in luggage, clothing, and furniture, making their way into homes. Once inside, they hide in various places, not just in beds. They can be found in box springs, bed frames, and even behind wallpaper.
Fleas are typically brought into the home by pets. They thrive in warm, humid environments and can also be found in carpets, pet bedding, and upholstered furniture. Unlike bed bugs, fleas are more prevalent during the warmer months.
Understanding the differences between bed bugs and fleas is crucial for effective pest control. While both are unwelcome guests in any home, their distinct characteristics require different approaches for prevention and eradication. Homeowners should be vigilant in identifying these pests early and take appropriate measures to ensure their homes remain safe and comfortable.
The Health and Home Impact of Bed Bugs and Fleas
The presence of bed bugs and fleas in a home extends beyond mere discomfort; these pests pose significant health and economic implications for homeowners. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective prevention and intervention.
Bed Bugs: While bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases directly, their bites can lead to a range of health issues. The Journal of Medical Entomology highlights that bed bug bites often result in allergic reactions, which can vary from mild to severe. In some cases, individuals experience intense itching, leading to excessive scratching and secondary skin infections. Moreover, the psychological impact of bed bug infestations is well-documented, with individuals reporting symptoms of anxiety, insomnia, and even post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in severe cases.
Fleas: Fleas, though tiny, are capable of causing significant health problems. The CDC notes that fleas can transmit several diseases to pets, such as cat scratch disease and tapeworms. In humans, flea bites can result in allergic reactions and, in rare cases, transmit diseases like typhus. Particularly concerning is the flea’s ability to act as a vector for various pathogens, potentially leading to more serious health concerns if not addressed promptly.
Economic Burden: The economic impact of pest infestations, particularly bed bugs and fleas, is substantial. Homeowners often face high costs in dealing with these pests, including professional pest control services, replacement of infested furniture, and sometimes even temporary relocation costs. The National Pest Management Association reports that the total annual cost of bed bug extermination in the U.S. runs into hundreds of millions of dollars, reflecting the extensive nature of these infestations.
Property Damage: Beyond the immediate cost of eradication, these pests can cause significant damage to property. Bed bugs, for instance, are known to infest not just beds but also furniture, clothing, and even electrical outlets, leading to a wide range of property damage. Fleas, while less likely to damage property directly, can infest carpets, pet bedding, and upholstery, necessitating costly cleaning or replacement.
Social Stigma: There is also a social aspect to consider. Infestations, particularly of bed bugs, often carry a social stigma, leading to embarrassment and isolation for affected individuals. This stigma can discourage people from seeking timely help, exacerbating the problem.
The health and home impact of bed bugs and fleas is far-reaching, affecting physical health, mental well-being, and financial stability. Awareness of these implications is essential for homeowners, not only for effective pest control but also for mitigating the broader effects these pests can have on their lives. As such, proactive measures, early detection, and prompt professional intervention are key to managing these unwelcome invaders.
Prevention and Control
Prevention and control are critical in the battle against bed bugs and fleas, as these measures are far more effective and less costly than dealing with a full-blown infestation.
Preventive measures are essential in keeping these pests at bay. For bed bugs, this includes regular inspections of sleeping areas, especially after traveling or purchasing second-hand furniture. Using protective covers on mattresses can also deter these pests from making a home in your bed. Flea prevention is primarily focused on pets; regular grooming and veterinarian-approved flea treatments can significantly reduce the risk of flea infestations in the home.
Regular cleaning and vacuuming are also vital. These simple practices can remove early stages of infestations, such as eggs or larvae, before they mature. Educating family members about the signs of bed bugs and fleas can also help in early detection, preventing a small problem from becoming a larger one.
Once an infestation is detected, control measures must be implemented swiftly. For bed bugs, this often involves a combination of chemical treatments and heat treatments, as these pests are notoriously resistant to many traditional pesticides. Flea infestations typically require thorough cleaning of all fabrics in the home, along with treatments for both the home and pets.
Professional pest control services are often necessary for complete eradication. These experts can provide targeted treatments and follow-up services to ensure that the infestation is fully resolved. They can also offer customized advice for preventing future infestations based on the specific conditions of your home.
Prevention and control are not just about dealing with pests; they are about maintaining a healthy, safe living environment. By prioritizing these measures, homeowners can protect their families, pets, and properties from the hidden dangers of bed bugs and fleas.
An In Depth Look at the Difference Between Bed Bugs and Fleas
| Feature | Bed Bugs | Fleas |
|---|---|---|
| Size | About the size of an apple seed (5-7 mm) | Smaller, about the size of a pinhead (1.5-3.3 mm) |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Shiny, reddish-brown |
| Shape | Oval and flat | Small and narrow |
| Mobility | Crawls quickly; cannot fly | Jumps long distances; cannot fly |
| Habitat | Prefer human environments; found in mattresses, furniture, and luggage | Often found on pets, as well as in carpets, pet bedding, and upholstered furniture |
| Feeding Habits | Nocturnal; feed on human blood | Feed on blood of both humans and animals |
| Bite Appearance | Bites often appear in a line or cluster, mainly on upper body | Bites usually on lower body, especially around ankles |
| Health Risks | Allergic reactions, potential psychological effects | Can transmit diseases to pets, rare transmission to humans |
| Reproduction | Female lays up to 5 eggs per day | Female lays up to 50 eggs per day, rapid reproduction |
| Seasonal Activity | Active year-round, with peak activity in warmer months | More active in warmer months, less so in colder periods |
| Detection | Difficult to spot; often require professional inspection | Easier to detect, especially on pets |
| Control Measures | Professional extermination, heat treatment, mattress encasements | Regular pet grooming, flea treatments, vacuuming |
Bed Bug Remediation Costs
- Initial Inspection: Many pest control companies offer free initial inspections, though some may charge a fee ranging from $50 to $200.
- Chemical Treatments: The most common method for bed bug extermination, chemical treatments typically cost between $300 and $1,000 per room. The total cost depends on the number of rooms treated and the severity of the infestation.
- Heat Treatments: This method involves heating the entire room or home to a temperature lethal to bed bugs. Prices for heat treatments can range from $800 to $2,500 or more, depending on the size of the area.
- Whole-House Fumigation: In severe cases, fumigation may be necessary. This can cost between $4,000 and $8,000, depending on the size of the home.
Flea Remediation Costs
- Initial Inspection: Similar to bed bugs, inspections for fleas may be free or cost up to $100.
- In-Home Treatments: Professional flea treatments for an average-sized home can range from $75 to $400. The cost can increase if follow-up treatments are required.
- Pet Treatments: Treating pets is an essential part of flea control. Costs for veterinary flea treatments can range from $40 to $200, depending on the type of treatment and the size of the pet.
- Yard Treatments: If fleas are found outside the home, yard treatments may be necessary, typically costing between $50 and $300.
Additional Considerations
- Location: Prices can vary significantly based geographic location.
- Severity of Infestation: More severe infestations often require more extensive and therefore more expensive treatments.
- Follow-up and Preventative Treatments: Regular maintenance treatments can add to the overall cost but are crucial for preventing re-infestation
A Comprehensive Approach to a Pest-Free Home
The battle against bed bugs and fleas is ongoing and multifaceted, requiring vigilance, knowledge, and proactive measures from homeowners. These tiny invaders, though small, can have outsized impacts on our health, well-being, and even our finances. Understanding their behavior, habitat, and the risks they pose is the first step in a comprehensive approach to maintaining a pest-free home.
Awareness is crucial. Homeowners should educate themselves about the signs of bed bug and flea infestations. Bed bugs leave behind telltale signs like small blood spots on sheets, a sweet musty odor, and their tiny, oval-shaped exoskeletons after molting. Fleas are often detected by their bites, which are typically concentrated around the ankles and legs, or by noticing pets scratching more than usual.
Preventive measures are far more effective and less costly than dealing with a full-blown infestation. Regular cleaning, including vacuuming carpets and furniture, can help remove any early invaders. Being cautious when bringing second-hand furniture into the home and using protective covers on mattresses can thwart bed bug infestations. For fleas, the focus should be on pet care, including regular baths and using veterinarian-recommended flea control products.
When prevention fails, early intervention is key. Homeowners should not hesitate to contact pest control professionals at the first sign of an infestation. These experts can provide a tailored approach, often combining chemical treatments with heat treatments or steam cleaning, to eradicate these pests. It’s important to act quickly, as delays can allow the infestation to grow, making it more challenging and expensive to control.
Managing bed bugs and fleas is not just an individual effort; it involves community awareness and support. Sharing information and strategies with neighbors can help prevent the spread of these pests. Local health departments and community organizations often provide resources and guidance for dealing with infestations, making them valuable allies in this fight.
Finally, a holistic approach to home and health is essential. This includes not only maintaining cleanliness and taking preventive measures but also understanding the potential psychological impact of infestations. Stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances are common in households dealing with bed bugs or fleas. Seeking support, whether through professional counseling or community support groups, can be an important aspect of dealing with these challenges.
The fight against bed bugs and fleas is a continuous process that demands awareness, prevention, and prompt action. By adopting a comprehensive approach that encompasses education, preventive strategies, timely intervention, community involvement, and a holistic view of health and well-being, homeowners can effectively protect their families and homes from these unwelcome guests. Remember, the key to a pest-free home lies not just in reacting to problems, but in anticipating and preventing them.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I tell if I have bed bugs or fleas in my home?
Bed bugs are small, reddish-brown, and oval-shaped, while fleas are smaller, darker, and more elongated. Bed bugs are often found in mattresses, furniture, and carpet edges, whereas fleas prefer to live on pets, in pet bedding, and in carpets.
Do bed bugs and fleas transmit diseases to humans?
Bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases to humans. However, their bites can cause allergic reactions and psychological distress. Fleas can carry and transmit diseases to pets, which can indirectly affect human health.
What are the signs of a bed bug infestation?
Signs include small, itchy bite marks on your skin, tiny blood spots on bedding, and dark specks (bed bug excrement) around bed frames, mattresses, and furniture.
How can I prevent bed bugs and fleas from infesting my home?
Regular cleaning, vacuuming, and inspecting second-hand furniture can prevent bed bugs. For fleas, regular pet grooming and using veterinarian-recommended flea treatments are effective.
Are over-the-counter sprays effective against bed bugs and fleas?
Over-the-counter sprays can be somewhat effective but are usually not sufficient for complete eradication. Professional pest control services are often necessary for a thorough treatment.
Can bed bugs and fleas live in clean homes?
Yes, both bed bugs and fleas can infest clean homes. Cleanliness can help in preventing infestations but is not a foolproof solution.
How do I treat bed bug or flea bites?
Most bites can be treated with over-the-counter anti-itch creams and antihistamines. If you experience severe reactions, consult a healthcare provider.
How long can bed bugs and fleas live without a host?
Bed bugs can survive for several months without feeding, while fleas can live for about a week to two weeks without a host.
Can bed bugs and fleas infest other areas of my home besides the bedroom?
Yes, while bed bugs are commonly found in bedrooms, they can infest living rooms and other areas. Fleas can be found anywhere in the home, especially if you have pets.
Should I throw away my mattress if I have bed bugs?
Not necessarily. Mattresses can often be treated and saved. Using mattress encasements and professional pest control services can eliminate bed bugs without discarding the mattress.